HTML-Lists
-
Ordered lists are lists where each item in the list is numbered. For example, the list might be a set of steps for a recipe that must be performed in order, or a legal contract where each point needs to be identified by a section number.
-
Unordered lists are lists that begin with a bullet point (rather than characters that indicate order).
-
Definition lists are made up of a set of terms along with the definitions for each of those terms.
-
<ol>
The ordered list is created with the <ol> element.
-
<li>
Each item in the list is placed between an opening <li> tag and a closing </li> tag. (The li stands for list item.)
Unordered Lists
-
<ul>
The unordered list is created with the <ul> element.
-
<li>
Each item in the list is placed between an opening <li> tag and a closing </li> tag. (The li stands for list item.)
Definition Lists
-
<dl>
The definition list is created with the <dl> element and usually consists of a series of terms and their definitions. Inside the <dl> element you will usually see pairs of <dt> and <dd> elements.
-
<dt>
This is used to contain the term being defined (the definition term).
-
<dd>
This is used to contain the definition.
Nested Lists
You can put a second list inside an <li> element to create a sublist or nested list. Browsers display nested lists indented further than the parent list. In nested unordered lists, the browser will usually change the style of the bullet point too.
There are three types of HTML lists: ordered, unordered, and definition.
Ordered lists use numbers.
Unordered lists use bullets.
Definition lists are used to define terminology.
Lists can be nested inside one another.
Border, Margin & Padding
1) Border
Every box has a border (even if
it is not visible or is specified to
be 0 pixels wide). The border
separates the edge of one box
from another.
2) Margin
Margins sit outside the edge
of the border. You can set the
width of a margin to create a
gap between the borders of two
adjacent boxes.
3) Padding
Padding is the space between
the border of a box and any
content contained within it.
Adding padding can increase the
readability of its contents.
CSS3: Border Images
border-image The border-image property applies an image to the border of any box. It takes a background image and slices it into nine pieces.
CSS3: Box Shadows box-shadow The box-shadow property allows you to add a drop shadow around a box. It works just like the text-shadow property that you met on page 288. It must use at least the first of these two values as well as a color:
Horizontal offset
Negative values position the
shadow to the left of the box.
Vertical offset
Negative values position the
shadow to the top of the box.
Blur distance
If omitted, the shadow is a solid
line like a border.
Spread of shadow
If used, a positive value will
cause the shadow to expand in
all directions, and a negative
value will make it contract.
CSS3: Rounded Corners
border-radius CSS3 introduces the ability to create rounded corners on any box, using a property called border-radius. The value indicates the size of the radius in pixels.
Java Script
ARRAY
An array is a special type of variable. It doesn’t just store one value; it stores a list of values.
##
SWITCH STATEMENTS
A switch statement starts with a variable called the switch value. Each case indicates a possible value for this variable and the code that should run if the variable matches that value.

USING DO WHILE LOOPS
The key difference between a whi 1 e loop and a do whi 1 e loop is that the statements in the code block come before the condition. This means that those statements are run once whether or not the condition is met.
If you take a look at the condition, it is checking that the value of the variable called i is less than 1, but that variable has already been set to a value of 1.
Therefore, in this example the result is that the 5 times table is written out once, even though the counter is not less than 1.
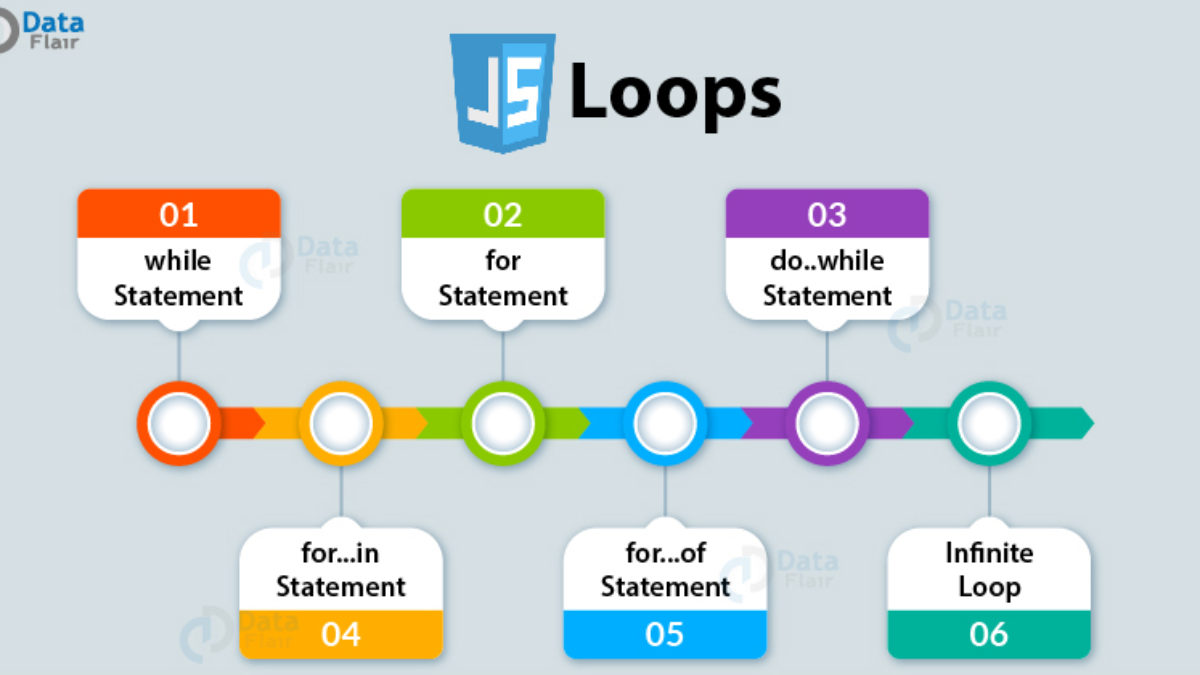
There are three types of loop: for, while, and do … while. Each repeats a set of statements.